Created by the Security Executive CouncilThe process to create a security master plan involves discussions across the enterprise. Security leaders can't do the kind of planning like they used to - it requires a more comprehensive view of the organization. What changed to make this so? There is no one "right" way to create a security program anymore. Every CEO has their own opinion of how to do "security". And on top of that there is now a huge diversity in organizational structure and leadership, which makes planning a very individualistic exercise.
In today's world, understanding an organization's corporate culture is everything. If the security leader does not get that right – the rest does not matter. Additionally, if the right key success factors have not been identified - they will never get key performance indicators (KPIs) right.
The process will be slightly different for any given organization based on industry, risk appetite, organizational structure, acceptable residual risk levels, etc. The chart below lists some of the main steps the SEC has identified for a successful plan. Notes: Some steps may happen concurrently or in a different order depending on circumstances. Also, this process should be revisited periodically.
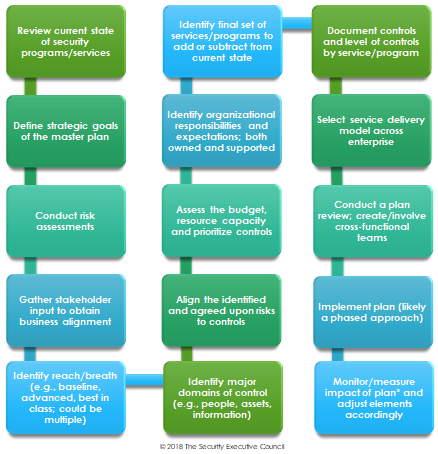
The need for monitoring and measuring the impact of the strategic master plan cannot be overlooked. KPI identification should be considered concurrently with plan development.
*
Program/Services KPI examples (Security owned and where Security supports):
- Elimination of sanctionable penalties associated with frequency and severity of compliance deviations.
- Better cross-functional collaboration results in faster time for investigation resolution.
- Percent of reduction of security-related incidents attributable to improved security measures.
- Percent of internal customer satisfaction survey scores above target.
- Percent conformance of budgeted activities to performance measures in annual plan.
- Reduction in security cost as a percent of revenue.
- Reduction in direct cost of security incidents or critical process disruptions.
- Reduction in cost of compliance with security-related regulations or cost to insure.
- Measurable reduction in cycle time or cost of essential security controls.
- Reductions in employee interaction with time-consuming security measures.
- Increased market penetration attributable to security measures; facilitating secure business process in risky markets.
- Percent reduction in employee on-boarding time attributable to vetting process improvement
- BI vetting processes identify revised HR screening routines that yield improved candidate identification
This is a high- level view of the process. We can work with you on the details and your strategic security master plan roadmap.
Contact Us to find out more.

